 |
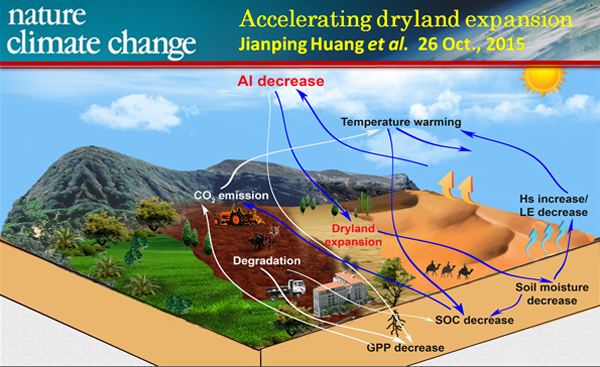
Arid and semi-arid areas are areas where precipitation cannot compensate for surface evaporation and vegetation transpiration. Currently, arid and semi-arid areas account for about 40% of the world's land surface area. Affected by human activities such as population growth, urbanization and climate change, arid and semi-arid areas will continue to expand globally. Studies have shown that most of the current climate system models cannot well simulate the extent of the expansion of arid and semi-arid regions in the world. By comparing observations and climate model simulations over the past 60 years, Professor Huang and his team confirmed that climate system models significantly underestimate the rate of global drought. They further used historical observational data to revise climate system model simulations to better reflect changes in global arid and semi-arid areas. Correction of the model data was used to predict the future secondary emission scenarios (RCP4.5) and high emissions scenario (RCP8.5) under arid and change characteristics of arid area, found that under the high emissions scenario, the 21st century compared arid half arid area in 1961-1990 climate area will increase by 23% on average, while 78% of arid and half arid area of expansion will take place in developing countries. The study also shows that the trend of warming in arid and semi-arid areas is significantly higher than that in humid areas, and the combined effects of climate warming, intensified drought and population growth will increase the risk of desertification in developing countries, thus further widening the regional differences in global economic development. The study adds to the growing awareness of the urgency of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating desertification globally.
Results link: http://www.nature.com/nclimate/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nclimate2837.html